AI agents are among the most highly debated enterprise technologies of 2025, garnering the attention of boardrooms and investors across various sectors. To executives and project managers, the urgency to roll out agent-based solutions has never been greater, as technology leaders are viewing revolutionary results in productivity and customer experience.
But market reality is much less advanced than hyped, as only 21% of senior managers have started implementation. This reveals an excitement-execution gap: most businesses are still investigating data readiness, governance, and business fit before effectively operationalising AI agents.
The Real Market Landscape of AI Agent Growth

The market for global AI agents is set to balloon from USD 7.92 billion in 2025 to a staggering USD 236 billion by 2034 at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 45.82%, according to Precedence Research. The fast pace of market growth indicates a growing need for automation and smart decision-making across industries, from finance and healthcare to customer care and IT operations.
AI agents provide adaptable, context-sensitive capabilities that go beyond the limitations of rule-based bots, enabling enterprises to automate intricate workflows and enhance responsiveness.
Top AI Agent Adoption Challenges
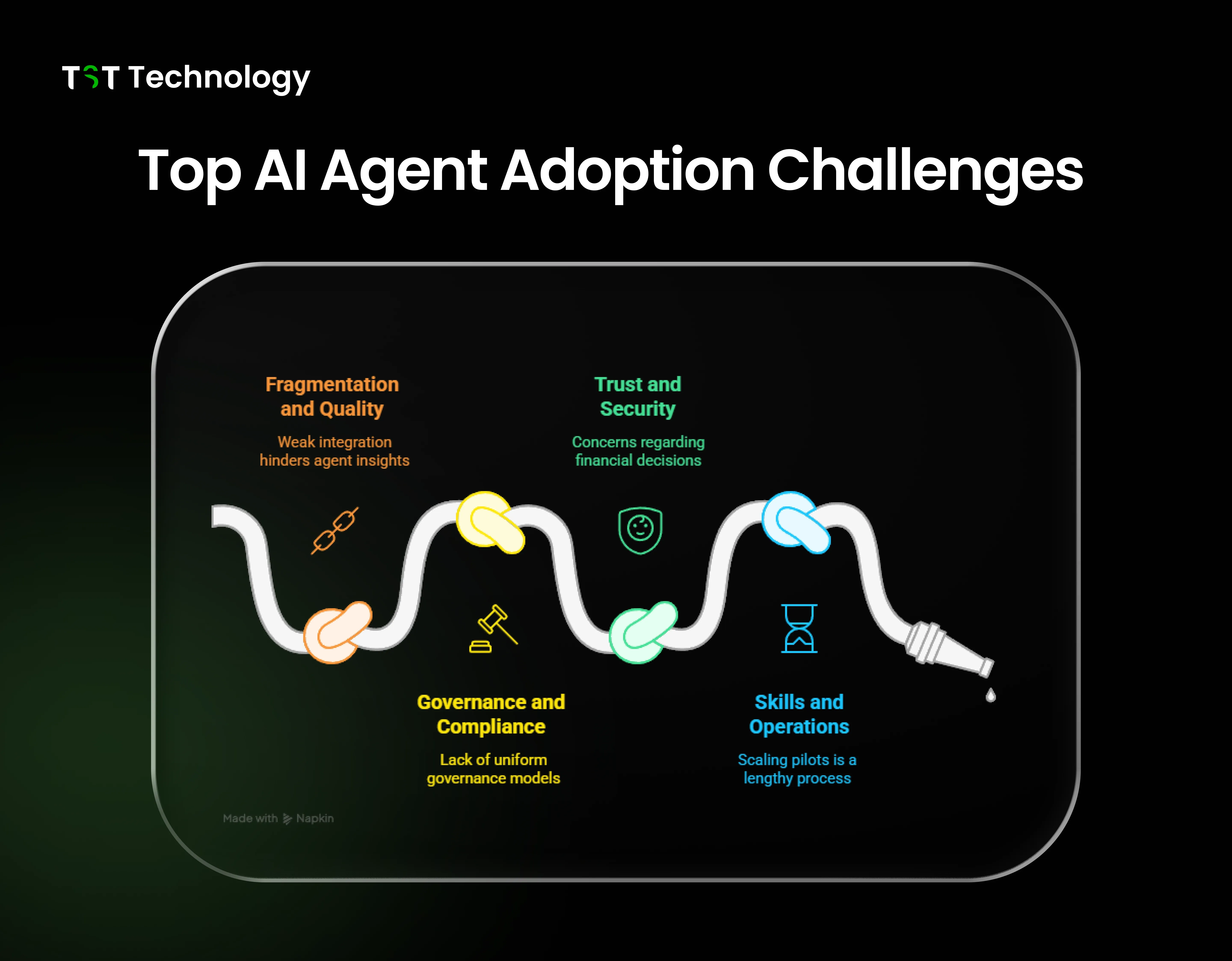
AI agent adoption, as a top enterprise initiative for 2025, still struggles with entrenched operational, data, and governance issues. Organisations are growing increasingly aware of the value of autonomous agents to change their businesses, but most are stalled by disjointed infrastructure, ambiguous accountability models, and nascent data environments.
The most prevalent blockers are:
- Fragmentation and quality concerns: Most companies suffer from fragmented systems and weak integration, hindering agents from gaining insights from integrated data streams.
- Uncertainty in governance and compliance: Agentic AI systems often lack uniform governance models, leaving companies uncertain about how to ensure explainability, ethical regulation, and global compliance.
- Trust and security risks: In its AI Agent Survey, PwC finds 28% of firms place trust and safety high among their top three issues, particularly regarding financial and autonomous decision-making processes.
- Skills and operational gaps: The absence of mature AI governance and orchestration professionals means scaling pilots to production is a lengthy process.
To break these obstacles, leaders need to marry technical readiness with business clarity- strong data pipelines, responsible AI architectures, and cross-functional collaboration from day one.
Adoption Metrics: Who's Really Using AI Agents?

78% of businesses apply AI to one or more business functions as of 2025, which is a high growth in adoption rate. Most organisations, though, are still deploying AI agents as pilot projects instead of as integrated core systems.
Among adopters, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMBs) dominate with 65% adoption rates, followed by 11% of large companies deploying AI agents across the board (Lyzr Report 2025). Adoption is mostly centred on sales, marketing, and customer support automation- areas where AI agents help with lead generation, personalised contact, and helpdesk functions. More advanced autonomous workflows are uncommon due to integration and governance complexities.
This trend indicates that companies are using AI agents to improve certain business processes, but only a limited number have achieved full operational maturity or disseminated AI agents to all departments.
Why 90% of Companies Are Still in Early Stages?
Most companies are hindered by huge barriers that remain in the initial phases of AI agent implementation, largely because of operational, data, and governance issues. One major challenge is that many companies don’t have clean, ready data or strict rules for managing it. Without good data and clear policies, AI systems can’t work properly or give reliable results.
Some other significant challenges are:
- Isolated pilot agents that are unable to integrate with current systems because of API constraints, security considerations, and compliance requirements.
- A knowledge gap for handling multi-agent orchestration and properly measuring AI ROI, making organizations unready to scale efforts.
- Doubt about trusted "agentic AI" models and governance approaches, particularly in regulated sectors, that retards adoption and confidence in such technologies.
These blockers show the complexity of transitioning from experimentation into full operational maturity.
Knowing the Slow Adoption Curve of AI Agents
In 2025, the AI agent adoption curve is slow mainly due to the fact that organisations are highly uncertain about use cases, ROI, and integration complexity. Most companies don't progress beyond LLM-based chatbots to more advanced task-autonomous agents that deliver real business impact.
Main adoption roadblocks are:
- Complexity of integration with legacy systems, such as CRM and ERP, typically requires heavy customisation and technical savvy.
- Limited ROI points of evidence, since most deployments of AI agents are less than one year old, and results are still being tabulated.
- The necessity of phased scaling, in contrast to waiting for immediate enterprise-wide adoption.
As encapsulated by the Salesforce Agentic Maturity Model of 2025:
Although agents may be deployed rapidly, scaling their deployment across the business requires a careful, phased process.
This process prioritises incremental advancement, maturity-level checks, and change management, which are imperative for overcoming readiness impediments and realising the full potential of AI agents.
Scaling Up from Pilot to Scale with AI Agents: An Actionable Roadmap
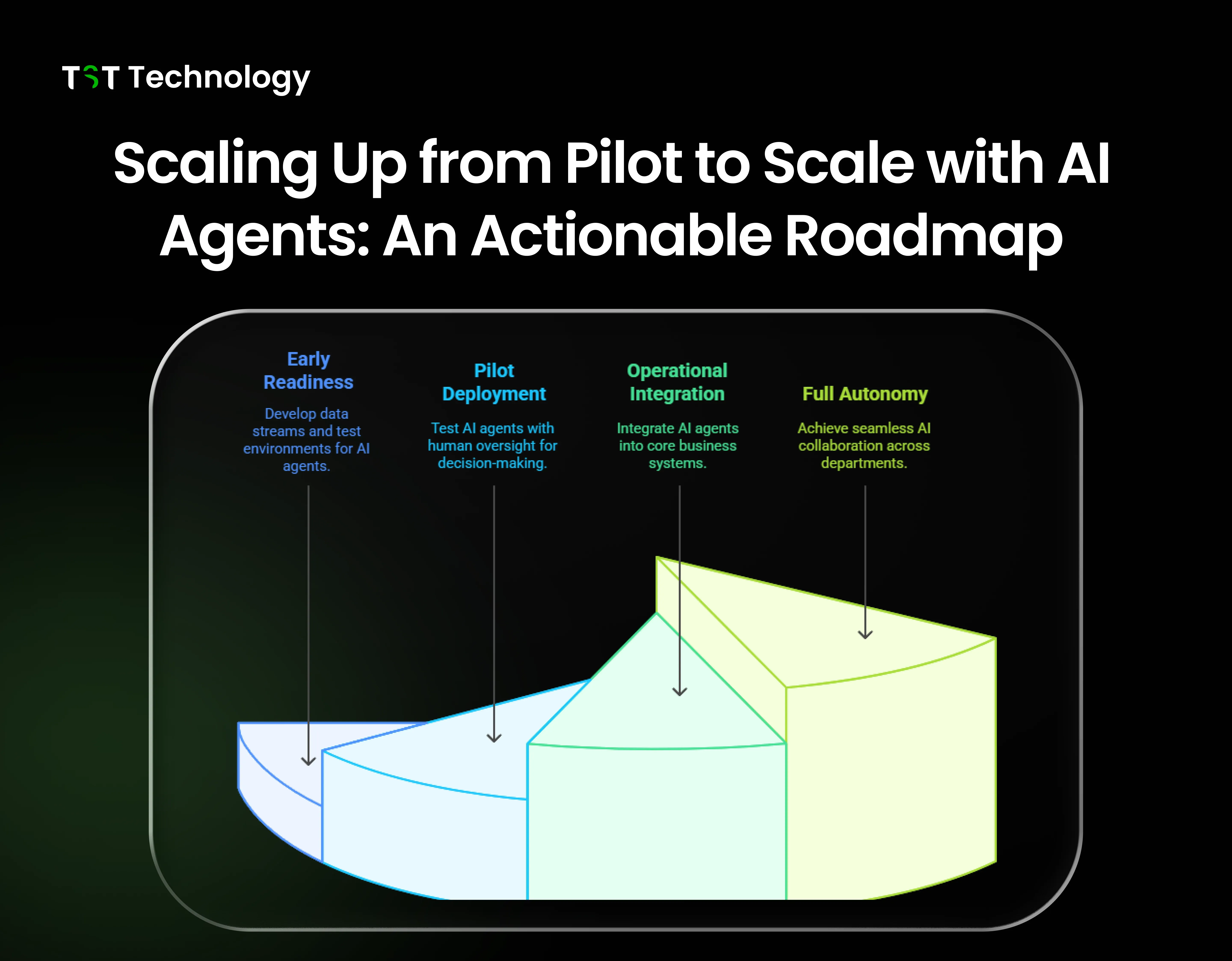
Scaling up from pilot to scale with AI agents calls for a phased, structured approach. The Agentic AI Maturity Model, as proposed by Salesforce and synthesised from industry models, is a well-defined roadmap for effectively maturing AI agent use in organisations.
- Early Readiness: Develop high-quality data streams, build open APIs, and establish safe test environments to accommodate controlled testing and evaluation of AI agents (Express Computer, 2025).
- Pilot Agent Deployment: Test business cases through the deployment of AI agents with human-in-the-loop for verifiable decision-making and risk reduction.
- Operational Integration: Integrate AI agents with core business systems such as CRM and ERP; measure performance and business outcomes on an ongoing basis to justify scaling efforts.
- Full Autonomy: Have enterprise-wide governance, risk management frameworks in place, and facilitate cross-departmental orchestration of agents to automate seamlessly and collaborate across functions.
This maturity model enables corporations to move step by step from small pilots to scalable, operational AI agents that can deliver sustainable business impact while keeping risks under strategic control.
If you want to scale your business with AI Agents, this pilot-to-production workflow is for you.
To get the full roadmap of integrating AI in your existing business, check out TST Technology’s AI business integration guide.
Conclusion
Readiness, not resources, differentiates early adopters of AI agents from those lagging behind. TST Technology assists companies in establishing these skills and expanding AI agents with established maturity models focusing on governance, integration, and stakeholder alignment. Our advisory and implementation services lead organisations through challenging adoption issues to deliver measurable value.
TST Technology can help you use AI Agents and make your company AI-forward. Book a free 30-minute consultation with our AI experts to get personalised guidance on the best strategy for your business.
Focus on readiness to transform AI from a buzzword into a business advantage.






